Chiropractic school angers FSU professors
Chiropractic school angers FSU professors
Some threaten to resign over the proposed school.
By RON MATUS, Times Staff Writer
Published December 29, 2004
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A growing number of professors in the Florida State University College of Medicine are saying they will resign if FSU administrators continue to pursue a proposed chiropractic school.
"I would no longer wish to volunteer my teaching energies to FSU medical school, should it encompass a school of chiropractic," wrote Dr. Ian Rogers, an assistant professor at FSU's Pensacola campus, in a Dec. 15 e-mail. "This is plainly ludicrous!!!!"
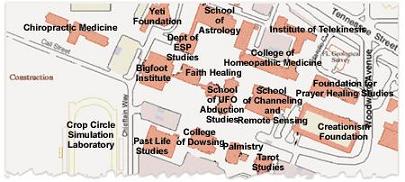
The threatened resignations - at least seven to date, all from assistant professors who work part time - reflect a belief among many in the medical establishment that chiropractic is a "pseudo-science" that leads to unnecessary and sometimes harmful treatments. Professors are even circulating a parody map of campus that places a fictional Bigfoot Institute, School of Astrology and Crop Circle Simulation Laboratory near a future chiropractic school.
But the professors' stance has a political aim, too.
Opposition is clearly mounting as the chiropractic school heads for crucial votes in January before the FSU board of trustees and the state Board of Governors.
In fact, the school is now seen as a test case for the fledgling Board of Governors, which critics have accused of kowtowing to Gov. Jeb Bush and the Legislature on the higher education issues it is supposed to oversee.
FSU was closed for the holidays Tuesday. FSU president T.K. Wetherell, provost Larry Abele and John Thrasher, chairman of the FSU board of trustees, could not be reached for comment.
But Sen. Dennis Jones, the Treasure Island Republican who spearheaded legislative support for the school in the spring, said the professors were "overreacting."
He accused anti-chiropractic groups from outside the state of stirring faculty opposition at FSU.
"If they resign, so be it," said Jones, a chiropractor himself. The instructors don't deserve to teach at FSU, he said, "if they're putting their credentials with people known for promoting professional bigotry."
The Legislature appropriated $9-million annually for the chiropractic school, which was pushed by Jones and then-Senate President Jim King, R-Jacksonville, an FSU graduate. It would be the only school of its kind in the country.
As supporters envision it, more than 100 new faculty members would train legions of chiropractors, with a special emphasis on Hispanic and African-American students. The school would also draw lucrative federal grants in alternative medicine.
Planning began years ago, but criticism didn't ramp up until after the legislative session.
Some opponents see the school as an end run around the Board of Governors, which oversees the state's 11 universities but has yet to consider the chiropractic school. Last week, a group headed by former university system chancellor E.T. York filed a lawsuit against the board, accusing it of failing to flex its constitutionally granted muscle and pointing to the chiropractic school as a prime example.
But some FSU faculty members are upset, too, fearing the school will shatter FSU's academic reputation. The list of critics include FSU's two Nobel laureates - Robert Schreiffer, a physicist, and Harold Walter Kroto, a chemist - and Robert Holton, the chemistry professor who developed the cancer-fighting drug Taxol, which has brought FSU tens of millions of dollars in royalties.
In recent weeks, more than 500 faculty members have signed petitions against the chiropractic school, including about 70 in the medical college, said Dr. Raymond Bellamy, an assistant professor who is leading the charge against the proposal. The medical college has more than 100 faculty members.
Some of them say they're willing to do more than sign a petition.
"I teach wonderful medical students from Florida State University here in Orlando," Dr. James W. Louttit wrote in an e-mail to Bellamy, who shared it with the St. Petersburg Times. "If they decide to start a chiropractic school I would no longer be able to support this program."
"It should come as no surprise that no major medical institution in this country, public or private, has embraced chiropractic medicine," wrote Dr. Henry Ho, a Winter Park physician and FSU assistant professor, in another e-mail. "If Florida State University were to do so, its fledgling attempt for credibility as a medical institution of stature would be severely jeopardized."
The situation at FSU isn't the first time chiropractors have sought to tie themselves to an established university.
In the late 1990s, faculty at York University in Toronto - one of Canada's largest schools - considered plans to affiliate with Canadian Memorial Chiropractic College. The plan would have brought York millions of dollars in new facilities and donations and given the chiropractic school academic credibility.
After a bitter, years-long fight, York faculty narrowly vetoed the plan in 2001.
At FSU, faculty have not officially voiced their concerns about the chiropractic school. Bellamy said they fear retaliation from lawmakers if they do.
"Everybody wants somebody else to kill it," he said.
Ron Matus can be reached at 727 893-8873 or matus@sptimes.com
[Last modified December 29, 2004, 00:19:14]
Some threaten to resign over the proposed school.
By RON MATUS, Times Staff Writer
Published December 29, 2004
[Times art]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A growing number of professors in the Florida State University College of Medicine are saying they will resign if FSU administrators continue to pursue a proposed chiropractic school.
"I would no longer wish to volunteer my teaching energies to FSU medical school, should it encompass a school of chiropractic," wrote Dr. Ian Rogers, an assistant professor at FSU's Pensacola campus, in a Dec. 15 e-mail. "This is plainly ludicrous!!!!"
The threatened resignations - at least seven to date, all from assistant professors who work part time - reflect a belief among many in the medical establishment that chiropractic is a "pseudo-science" that leads to unnecessary and sometimes harmful treatments. Professors are even circulating a parody map of campus that places a fictional Bigfoot Institute, School of Astrology and Crop Circle Simulation Laboratory near a future chiropractic school.
But the professors' stance has a political aim, too.
Opposition is clearly mounting as the chiropractic school heads for crucial votes in January before the FSU board of trustees and the state Board of Governors.
In fact, the school is now seen as a test case for the fledgling Board of Governors, which critics have accused of kowtowing to Gov. Jeb Bush and the Legislature on the higher education issues it is supposed to oversee.
FSU was closed for the holidays Tuesday. FSU president T.K. Wetherell, provost Larry Abele and John Thrasher, chairman of the FSU board of trustees, could not be reached for comment.
But Sen. Dennis Jones, the Treasure Island Republican who spearheaded legislative support for the school in the spring, said the professors were "overreacting."
He accused anti-chiropractic groups from outside the state of stirring faculty opposition at FSU.
"If they resign, so be it," said Jones, a chiropractor himself. The instructors don't deserve to teach at FSU, he said, "if they're putting their credentials with people known for promoting professional bigotry."
The Legislature appropriated $9-million annually for the chiropractic school, which was pushed by Jones and then-Senate President Jim King, R-Jacksonville, an FSU graduate. It would be the only school of its kind in the country.
As supporters envision it, more than 100 new faculty members would train legions of chiropractors, with a special emphasis on Hispanic and African-American students. The school would also draw lucrative federal grants in alternative medicine.
Planning began years ago, but criticism didn't ramp up until after the legislative session.
Some opponents see the school as an end run around the Board of Governors, which oversees the state's 11 universities but has yet to consider the chiropractic school. Last week, a group headed by former university system chancellor E.T. York filed a lawsuit against the board, accusing it of failing to flex its constitutionally granted muscle and pointing to the chiropractic school as a prime example.
But some FSU faculty members are upset, too, fearing the school will shatter FSU's academic reputation. The list of critics include FSU's two Nobel laureates - Robert Schreiffer, a physicist, and Harold Walter Kroto, a chemist - and Robert Holton, the chemistry professor who developed the cancer-fighting drug Taxol, which has brought FSU tens of millions of dollars in royalties.
In recent weeks, more than 500 faculty members have signed petitions against the chiropractic school, including about 70 in the medical college, said Dr. Raymond Bellamy, an assistant professor who is leading the charge against the proposal. The medical college has more than 100 faculty members.
Some of them say they're willing to do more than sign a petition.
"I teach wonderful medical students from Florida State University here in Orlando," Dr. James W. Louttit wrote in an e-mail to Bellamy, who shared it with the St. Petersburg Times. "If they decide to start a chiropractic school I would no longer be able to support this program."
"It should come as no surprise that no major medical institution in this country, public or private, has embraced chiropractic medicine," wrote Dr. Henry Ho, a Winter Park physician and FSU assistant professor, in another e-mail. "If Florida State University were to do so, its fledgling attempt for credibility as a medical institution of stature would be severely jeopardized."
The situation at FSU isn't the first time chiropractors have sought to tie themselves to an established university.
In the late 1990s, faculty at York University in Toronto - one of Canada's largest schools - considered plans to affiliate with Canadian Memorial Chiropractic College. The plan would have brought York millions of dollars in new facilities and donations and given the chiropractic school academic credibility.
After a bitter, years-long fight, York faculty narrowly vetoed the plan in 2001.
At FSU, faculty have not officially voiced their concerns about the chiropractic school. Bellamy said they fear retaliation from lawmakers if they do.
"Everybody wants somebody else to kill it," he said.
Ron Matus can be reached at 727 893-8873 or matus@sptimes.com
[Last modified December 29, 2004, 00:19:14]

<< Home